TL;DR:Baidu has developed a new AI Search Paradigm powered by a team of specialized agents that work together to answer complex queries. This system handles multi-step reasoning, adapts to failed searches, and mimics human thought processes better than traditional keyword or RAG-based search engines.
The Limitations of Today’s Search Engines
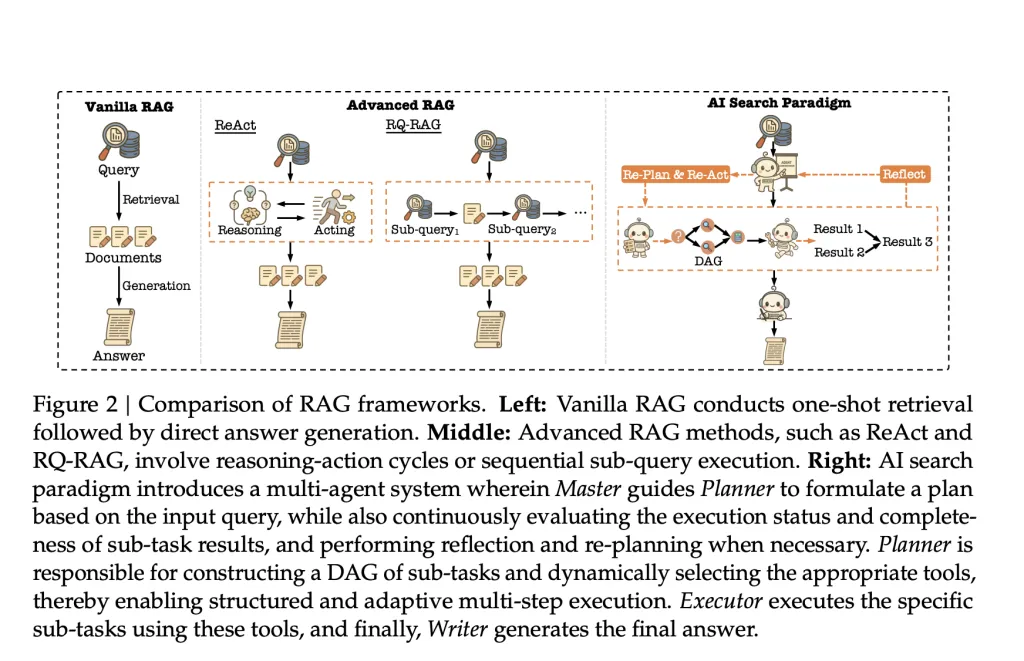
Search engines are constantly evolving, but most still struggle when faced with complex or layered questions. Even advanced tools that use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) tend to follow rigid steps. They can retrieve and summarize, but when it comes to reasoning or comparing data across multiple sources, they often fall short.
For example, asking “Who lived longer between Julius Caesar and Emperor Wu of Han?” is more than just a search query. It requires gathering data from different places, doing the math, and then comparing results. Most current systems cannot manage that kind of task effectively because they lack planning and adaptability.
Baidu’s Multi-Agent AI Search Framework
To tackle these challenges, Baidu researchers introduced a new model called the AI Search Paradigm. Rather than relying on a single AI agent, this approach uses a collaborative team of four intelligent agents:
- Master: Oversees the entire process and determines the approach based on the query’s complexity
- Planner: Breaks complex questions into smaller sub-queries
- Executor: Finds and uses the right tools to fetch or compute the answers
- Writer: Combines the results into a final, coherent response
This setup allows the system to mimic human-like search behavior, adapting to unexpected issues and refining its steps along the way.
How the System Thinks Like a Human
At the core of Baidu’s approach is something called a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). This is essentially a smart flowchart that organizes sub-tasks in a way that respects logical order. For every query, the Planner builds this graph to map out what needs to happen and when.
The Executor then performs each sub-task using tools selected from Baidu’s cloud infrastructure. If a tool fails or the result is unclear, the system adjusts and retries with alternatives. This dynamic planning avoids dead ends and ensures the answer is as complete as possible.
The Writer then steps in to check the quality of the data, resolve any inconsistencies, and compose the final result in a way that makes sense to the user.
Real-World Example: Caesar vs. Emperor Wu
One of the test cases for this system involved comparing the lifespan of Julius Caesar and Emperor Wu of Han. The Planner broke the query into three steps:
- Retrieve the birth and death years of Emperor Wu
- Retrieve the same for Julius Caesar
- Calculate and compare their ages
The Executor used separate tools to fetch the data, and the Writer synthesized the result: Emperor Wu lived for 69 years, while Caesar lived for 56. The system correctly determined that Wu lived 13 years longer.
This level of reasoning and coordination is something that traditional RAG systems, which retrieve information in a single pass, cannot handle well.
Smarter Search Is Becoming a Reality
This new AI Search Paradigm represents a major step forward in making machines understand questions like humans do. Instead of relying on a single shot of retrieval and hoping for the best, Baidu’s multi-agent system reflects, adapts, and collaborates throughout the entire process.
By breaking complex questions into smaller parts, using the right tools for each job, and reassembling the answers into a clear result, this architecture opens the door to much more intelligent and scalable search engines.